Ultimate Guide to Understanding Bear Behavior and Ensuring Your Safety in the Wild
Dive into the Distinctive Traits of Various Bear Species
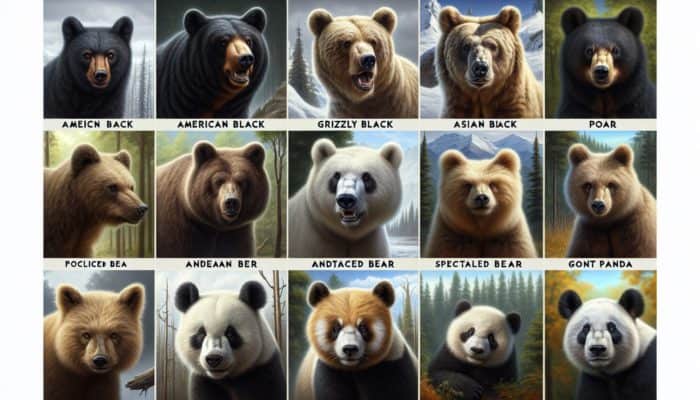

Understanding how to survive a bear encounter hinges on your knowledge of the various species of bears, which is vital for anticipating their behavior and interactions with humans. Worldwide, there are eight unique species of bears: American black bears, grizzly bears, polar bears, Asian black bears, Andean bears, spectacled bears, sloth bears, and giant pandas. Each species possesses distinctive traits that significantly shape their behavior, especially regarding human interactions and the environments they inhabit. For instance, black bears are generally recognized for their timid nature and inclination to steer clear of human presence, while grizzly bears are typically more aggressive and protective, especially when their young or food sources are threatened. Additionally, polar bears, which predominantly roam the Arctic, are adept at hunting seals and may pose serious risks during human encounters. Familiarizing yourself with the species prevalent in your area, such as the common grizzly in North America or the numerous black bears inhabiting many wooded regions, will enhance your ability to respond effectively in the event of an encounter.
Prior to venturing into bear territory, identifying the specific species of bear can greatly bolster your safety. Observing a bear’s color and size can provide initial clues; typically, black bears are smaller and have a more slender build compared to grizzly bears, which are larger and easily recognized by their notable shoulder humps. Gaining insight into these distinctions not only prepares you for possible encounters but also helps you understand the particular dangers linked with each bear type. Knowledge about the various bear species is a fundamental aspect of wilderness safety, empowering you to make informed decisions while navigating their habitats.
Recognising Bear Aggression: Key Signs for Your Safety
Identifying the signs of an aggressive bear is crucial for ensuring your safety while exploring the wilderness. Aggressive bears may display a range of behaviors, including jaw popping, huffing, and bluff charges. Jaw popping often indicates agitation, where the bear snaps its jaws together as a sign of discomfort or irritation. Huffing, characterized by loud exhalations, shows that a bear feels threatened; meanwhile, a bluff charge occurs when the bear rushes towards you to assess your reaction. If you notice any of these warning signs, it’s essential to stay calm and carefully evaluate the situation.
What steps should you take if a bear shows signs of aggression? First and foremost, do not run. Bears are remarkably fast and can easily outrun humans, which may trigger their instinct to chase. Instead, make yourself appear larger and more intimidating. Speak firmly and clearly to the bear while gradually backing away, ensuring not to turn your back on it. If the bear continues to approach, be prepared to use bear spray as a deterrent. Always maintain a safe distance and avoid direct eye contact, as this may be interpreted as a challenge. Recognizing these aggressive behaviors and knowing how to respond appropriately can significantly enhance your chances of a safe outcome during an encounter.
Understanding Bear Habitats: Enhancing Your Safety
Bears inhabit a variety of environments, each defined by unique characteristics that greatly influence their behavior and interactions with humans. Comprehending the preferred habitats of different bear species can assist you in avoiding potential encounters. For example, black bears are often found in forests, swamps, and mountainous regions, where they can readily access food sources like berries, nuts, and insects. In contrast, grizzly bears generally prefer areas that offer a mix of dense forests and open meadows, allowing them to forage for a diverse diet.
Being aware of these habitats enables you to plan your outdoor activities in a way that minimizes bear encounters. For instance, if you are hiking along trails known for bear activity, it’s crucial to choose times of day when bears are less active, such as midday during warmer months. Moreover, understanding the seasonal behaviors of different bear species, like their movements during salmon spawning or the ripening of berries, can help guide you in avoiding areas likely to attract them. Recognizing bears’ habitats and behaviors represents a proactive strategy for wilderness safety that can significantly reduce the risk of encounters.
Investigating Bear Diets and Foraging Habits
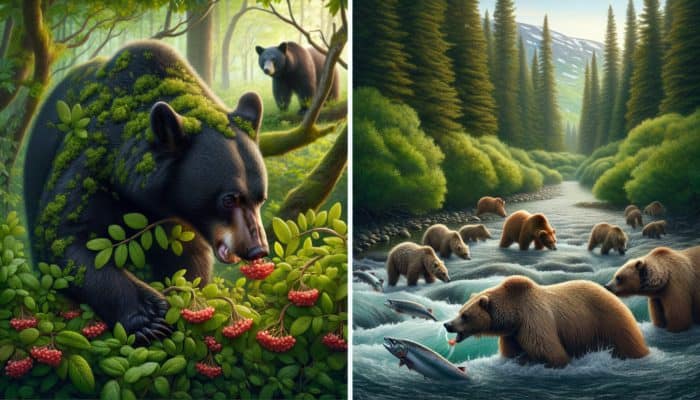

The dietary patterns and foraging behaviors of bears provide essential insights into their movement and potential interactions with humans. Bears are omnivorous, and their diets can vary significantly based on geographic location and seasonal changes. In North America, for instance, black bears typically consume a mix of plants, fruits, and small mammals, while grizzly bears may rely heavily on salmon during spawning seasons. Understanding what bears eat can help predict where they might be found and during which times they are most active.
During spring, bears awaken from hibernation and actively seek fresh plant growth, increasing their likelihood of being encountered in lush areas. Conversely, in late summer and autumn, bears are often seen around berry patches or salmon runs, where food is abundant. Familiarity with these foraging behaviors can assist outdoor enthusiasts in wisely planning their activities, steering clear of areas experiencing heightened bear activity. The more knowledge you possess about the diets and foraging habits of bears, the better equipped you will be to avoid unintentional encounters with these magnificent creatures.
Professional Insights for Safely Navigating Bear Encounters
Analyzing Bear Attack Statistics for Greater Awareness
Statistics related to bear attacks can offer invaluable insights into the frequency and outcomes of human-bear interactions, emphasizing the importance of preparation and awareness. Here are some key statistics that highlight this aspect:
- On average, there are approximately 1-2 fatal bear attacks in North America each year.
- Black bears account for the majority of bear attacks; however, encounters with grizzly bears often lead to more severe consequences.
- Most bear attacks occur when a bear is unexpectedly surprised, typically due to hikers or campers inadvertently entering bear territory.
- Over 90% of bear encounters can be avoided through proper precautions and awareness of bear behavior.
These statistics underscore the necessity for outdoor enthusiasts to comprehend bear behavior and implement safety measures that are designed to minimize encounters. While bear attacks are relatively rare, the consequences can be severe. Familiarity with these statistics fosters a greater respect for wildlife and highlights the importance of responsible outdoor practices.
Proven Strategies for Preventing Bear Encounters
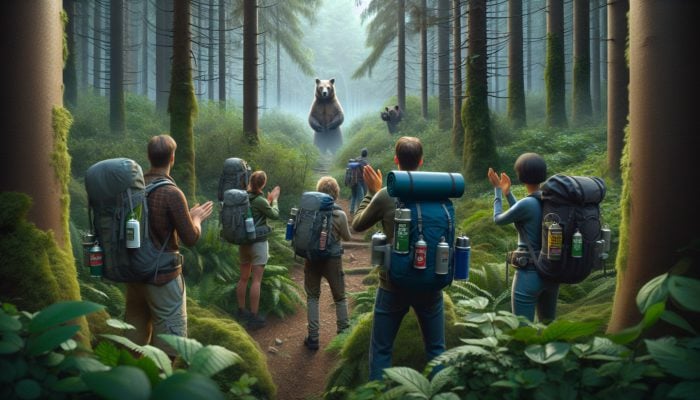

Experts recommend several impactful strategies to prevent bear attacks and improve overall safety while in bear habitats. One of the most effective methods is to make noise while hiking, which alerts bears to your presence and allows them to avoid you. This can include talking, clapping your hands, or using bear bells. Additionally, carrying bear spray is highly advisable, as it serves as a powerful deterrent that can stop an aggressive bear in its tracks when deployed correctly.
Moreover, another effective strategy is to avoid hiking alone. Traveling in groups significantly reduces the risk of bear encounters, as bears are less likely to approach larger groups of individuals. Furthermore, properly storing food and waste is crucial. Utilizing bear-proof containers and hanging food at least 10 feet off the ground and 4 feet from tree trunks can deter bears from being attracted to your campsite. These preventative strategies not only enhance safety but also contribute to a more enjoyable wilderness experience for all involved.
Survival Techniques to Apply During Bear Encounters
During a bear attack, employing specific survival techniques can significantly enhance your chances of survival. The first technique to consider is to play dead if attacked by a grizzly bear, as this may convince the bear that you are no longer a threat, leading it to cease its attack. However, should a black bear attack, it is generally recommended to fight back, as these bears tend to be less aggressive than their grizzly counterparts and often retreat when faced with resistance.
To effectively play dead, lie flat on your stomach with your hands clasped behind your neck. This position protects your vital areas while remaining still until the bear leaves the vicinity. If the bear persists in its assault, you may need to change your approach. Evaluate the situation; if the bear seems determined to continue its attack, fighting back may become necessary. Target vulnerable areas, such as the bear’s nose or eyes. Understanding when and how to utilize these survival strategies is crucial for anyone venturing into bear habitats, as it can mean the difference between life and death.
Preparing Thoroughly for Bear Encounters: Essential Steps
Critical Equipment to Enhance Your Safety from Bears
Equipping yourself with the right gear is vital for ensuring your safety in bear territory. Essential items to include are bear spray, which should always be easily accessible rather than stored away in a backpack. Familiarizing yourself with how to operate it before entering bear territory is crucial, ensuring you know how to use it effectively. Additionally, noise makers, such as bear bells or whistles, are useful tools for alerting bears to your presence.
Other important items include a comprehensive first-aid kit to quickly address injuries, and a sturdy walking stick, which can serve as a defensive tool if necessary. Proper clothing, such as brightly colored or odor-proof layers, can also deter interactions by making you less appealing to bears. Equipping yourself with this essential gear creates a safer environment and boosts your confidence while exploring wilderness areas, enabling you to engage with nature more fully.
The Importance of Training and Education on Bear Safety
Educating yourself about bear behavior and participating in training programs can significantly enhance your preparedness for potential encounters. Familiarizing yourself with bear awareness resources is essential. Many parks and wildlife organizations offer educational programs aimed at teaching effective safety practices in bear territory. These programs typically cover topics such as bear identification, behavior recognition, and emergency response techniques.
A bullet list of recommended training and education resources includes:
- Local wildlife organizations.
- National park services’ visitor centers.
- Outdoor survival courses focused on wildlife safety.
- Workshops and seminars dedicated to bear safety.
Investing your time in these resources not only enhances your preparedness but also fosters respect and understanding for wildlife, contributing to safer outdoor experiences for all.
Understanding Group Dynamics for Enhanced Bear Safety
Traveling in groups can deter bears and provide safety in numbers, making group dynamics an important aspect of bear safety. Bears are more likely to avoid larger groups of people, perceiving them as more threatening. Understanding how group size affects bear encounters is crucial; larger groups should maintain greater distances and make more noise to announce their presence in bear territory.
It is also essential to establish roles within the group, such as designating a leader who can navigate and keep track of everyone. Communication is vital, particularly to ensure everyone is aware of the safety protocols. Implementing a buddy system can further enhance safety by providing support and heightened alertness among group members. When managed effectively, group dynamics can significantly reduce the risk of bear encounters and enhance overall safety for all participants.
Recognising Bear Behavior for Effective Management of Encounters
Recognizing bear behavior is essential for safely managing encounters in the wilderness. Understanding body language and vocalizations can help you gauge a bear’s mood and intentions. For instance, a bear that stands on its hind legs is often merely trying to gather information rather than displaying aggression. Conversely, bears that snarl or emit aggressive vocalizations should be taken seriously and approached with caution.
What signs should you look for to assess a bear’s mood? Pay attention to these indicators:
- Body posture: relaxed versus tense.
- Vocalisations: huffs or growls.
- Ear position: Flattened ears indicate aggression.
- Movement: slow, cautious movements suggest curiosity.
Understanding these signs enables you to react appropriately during encounters, significantly increasing your chances of achieving a safe outcome while navigating bear territory.
Implementing Essential Safety Protocols and Procedures
Familiarity with safety protocols is crucial for effectively managing bear encounters. Knowing the proper use of bear spray is essential; ensure it is readily accessible, and that you understand how to operate it under pressure. Generally, the recommended steps during a bear encounter include:
- Remain calm and assess the situation.
- Do not run; instead, back away slowly.
- Make noise to alert the bear to your presence.
- If the bear approaches, use bear spray as a deterrent.
Having a clear plan of action can help manage your response effectively. Practicing scenarios with your group can enhance readiness and ensure everyone knows their role during an encounter. Implementing these safety protocols greatly increases your chances of a favorable outcome, ensuring that you and your companions can enjoy the wilderness safely.
Immediate Actions to Take During a Bear Encounter
Initial Reactions When Spotting a Bear
Your first response upon spotting a bear can significantly influence the encounter’s outcome. Remaining calm is paramount; panicking can lead to poor decision-making. Upon seeing a bear, evaluate its behavior and the surrounding environment. If the bear appears calm and does not seem to be advancing, slowly back away while keeping your eyes on the bear at all times.
What should your first actions be upon encountering a bear? First, avoid direct eye contact, as this can be perceived as a challenge. Next, calmly and firmly speak to the bear using a loud but non-threatening voice. This approach helps establish your presence without provoking a response from the bear. If the bear continues to approach, be ready to use bear spray. Remember, many encounters can be resolved without escalating the situation, so maintaining composure is critical for your safety.
Maximizing the Effectiveness of Bear Spray During Encounters
Bear spray is one of the most effective deterrents available and can be a lifesaver during an encounter. To use bear spray effectively, first ensure it is easily accessible. When the bear is approximately 30 feet away, remove the safety tab and aim slightly downward, as the spray will travel upwards. Deploy a cloud of spray towards the bear’s face while maintaining your ground.
Understanding the correct procedure is vital for maximizing its effectiveness. The ideal range for bear spray is typically around 25 feet, so ensure your canister is fully charged before entering bear territory. Familiarizing yourself with how to use bear spray properly can be a critical skill that may save your life in these situations.
Strategies for Playing Dead During a Bear Attack
In specific scenarios, playing dead can be an effective survival strategy when faced with a bear attack. This technique is particularly relevant when dealing with a grizzly bear, as it might view you as non-threatening and cease its attack.
When should you contemplate playing dead during a bear encounter? If a grizzly bear makes contact and escape is impossible, lie flat on your stomach with your hands clasped behind your neck. Spread your legs to make it more challenging for the bear to flip you over. Remain still and silent until the bear leaves the area. This act of submission can sometimes lead to a de-escalation of aggression. However, if a black bear attacks, it is generally recommended to fight back. Knowing when to employ each strategy can significantly impact your chances of survival.
Physical Defense Strategies Against Bear Attacks
Recognizing When to Fight Back Against a Bear
If a bear continues to attack and escape is not an option, fighting back may become necessary. Knowing when and how to do this can be life-saving. For instance, if a bear is persistently aggressive or has cornered you, it is crucial to shift into defense mode.
When is it appropriate to fight back against a bear? If a bear attacks you and you have exhausted all other options, aim for its vulnerable areas. It’s important to target the bear’s eyes and nose, as these areas are sensitive and may deter further aggression. Your objective should be to create an opportunity to escape rather than to harm the bear. Always remember that fighting should be a last resort; avoidance and de-escalation should be your first strategies when confronted by a bear.
Targeting Vulnerable Areas During a Bear Confrontation
During a physical confrontation with a bear, knowing where to strike can make a critical difference in your chances of survival. Targeting the bear’s eyes and nose can be effective in deterring it. These areas are sensitive and can prompt the bear to retreat.
What are the most vulnerable areas on a bear to target? Focus on:
- The eyes: a well-aimed jab can cause pain and deter the bear.
- The nose: striking this area can trigger a strong instinct for the bear to recoil.
- The ears, while harder to reach, can distract the bear from any trauma.
- A direct hit to the throat can incapacitate the bear temporarily.
Utilizing these tactics can increase your chances of survival during an encounter. However, keep in mind that evasion and non-confrontational strategies are always preferable to confrontation.
Using Available Objects for Defense Against Bears
In a confrontational scenario, using available objects can help defend yourself against a bear. Everyday items can serve as improvised weapons, enhancing your chances of survival.
Items that can be utilized as weapons against bears include:
- Sticks: can be used to poke at a bear if it gets too close.
- Rocks: throwing them can create noise and deter the bear.
- Backpacks: when used strategically, can provide distance.
- Any sharp object, such as knives or tools, can be employed if combat is unavoidable.
These objects can provide a critical advantage if you find yourself in a dire situation. However, always remember that the best defense is to avoid encounters altogether whenever possible.
Post-Encounter Actions Following a Bear Encounter
Assessing Injuries After a Bear Encounter
After a bear encounter, quickly assessing any injuries is crucial. Knowing basic first aid can significantly impact your ability to manage injuries effectively. If you have sustained any bites, scrapes, or bruises, evaluating their severity is essential.
What are the first steps to take after a bear attack? First, ensure you are safe from further bear encounters. Once secure, assess any visible wounds. Clean minor cuts and scrapes with water and apply a sterile bandage. For more serious injuries, such as deep lacerations or bites, applying pressure to stop any bleeding is vital. If the injuries appear severe, seek immediate medical attention. Being knowledgeable about how to assess injuries can be life-saving and can help guide your subsequent actions.
The Importance of Reporting Bear Encounters
Reporting bear encounters to the appropriate authorities is crucial for preventing future incidents. This action not only assists wildlife officials in tracking bear activity but also informs other outdoor enthusiasts about potential dangers in the area.
How should you report a bear encounter? Contact local wildlife management authorities as soon as possible. Provide them with details about the encounter, including the location, time, and any notable behavior exhibited by the bear. This information is invaluable for assessing bear populations and patterns, which may lead to increased safety measures in the area. Reporting incidents contributes to community safety and enhances awareness around bear behavior, ultimately fostering a healthier coexistence between humans and wildlife.
Seeking Medical Attention After a Bear Attack
Acquiring immediate medical attention following a bear attack is essential, even if injuries seem minor. The trauma of an attack can lead to complications that may not be immediately apparent.
What are the signs that you need immediate medical attention? Signs include severe bleeding, deep lacerations, indications of infection, or any difficulty breathing. Even if you feel fine initially, consulting a healthcare professional is wise. Additionally, being checked for rabies or other infections is necessary, especially in cases of bites. Prioritizing your health after an encounter with a bear ensures your well-being and prepares you for any long-term recovery processes that may be required.
Research-Backed Advantages of Surviving a Bear Attack
Fostering Psychological Resilience Through Survival Experiences
Surviving a bear attack can lead to the development of psychological resilience and coping mechanisms. The experience, while traumatic, often cultivates strength and the ability to manage stress in various aspects of life.
Expert analysis of the psychological effects of surviving a bear attack reveals that individuals frequently report changes in their approach to challenges. Many survivors find themselves more aware of their surroundings and more appreciative of nature, fostering a deeper connection with the outdoors. Such resilience can translate into improved mental health and the capacity to face future adversities with greater confidence and composure.
Promoting Community Awareness and Safety Initiatives
Survivors of bear encounters can play a vital role in raising awareness about bear safety and prevention, benefiting their communities. Sharing personal experiences helps educate others about the importance of understanding bear behavior and safety practices.
How can survivors contribute to community bear safety? By participating in local wildlife education programs or sharing their stories at community events, survivors can inspire proactive safety measures among outdoor enthusiasts. They can also assist in developing safety campaigns that emphasize bear awareness, ultimately leading to a more informed public. Engagement within the community fosters a collective responsibility toward wildlife safety and conservation, encouraging everyone to act responsibly when in bear habitats.
Personal Growth and Transformation After a Bear Encounter
The experience of surviving a bear attack can lead to significant personal growth and a deeper appreciation for life. Confronting such a life-threatening situation often reshapes perspectives and priorities.
What aspects of personal growth can emerge from surviving a bear attack? Many survivors report enhanced gratitude for everyday experiences, newfound respect for nature, and a desire to educate others about wildlife safety. This transformative experience can lead to increased empathy toward both humans and animals, fostering a more profound understanding of interconnectedness within the ecosystem. Personal growth resulting from survival situations often encourages individuals to become advocates for wildlife conservation and safety, sharing their knowledge and experiences to benefit others.
Implementing Sustainable Strategies for Bear Safety
Effective Habitat Management Techniques to Minimize Conflicts
Proper management of bear habitats is essential for reducing human-bear conflicts. By understanding bears’ natural behaviors and habitat preferences, we can implement strategies designed to keep both wildlife and humans safe.
What are effective habitat management strategies? Establishing bear-free zones, particularly in areas with high human activity, is crucial for maintaining safety. Additionally, encouraging local communities to use bear-proof trash containers and proper food storage methods can minimize bear attraction to residential areas. Educating the public about the importance of maintaining clean campsites and hiking trails can also contribute to safer coexistence. Effective habitat management reduces the risk of encounters and creates a balanced relationship between humans and bears, benefiting both parties.
Community Education Campaigns for Improved Bear Safety
Educating the public on bear safety can prevent future encounters and attacks. Awareness campaigns can significantly influence community behavior and attitudes towards wildlife, fostering a culture of respect and understanding.
How can public education campaigns reduce bear attacks? By providing clear, actionable information on bear behavior and safety practices, communities can cultivate a culture of awareness. Campaigns may include workshops, informational materials, or local events that engage residents and outdoor enthusiasts. Utilizing social media and local news outlets can amplify these messages, enhancing community engagement and encouraging responsible behavior in bear territory. Proactive public education campaigns are vital for long-term safety and coexistence with wildlife.
The Significance of Policy and Legislation in Bear Management
Implementing policies and legislation can help manage bear populations and human interactions effectively. Well-crafted policies can lead to improved safety protocols and resource allocation for wildlife management.
What policies can assist with long-term bear safety? Areas with high bear populations may benefit from regulations that include strict food storage requirements in national parks and wildlife reserves. Additionally, establishing educational requirements for visitors to bear habitats can enhance safety. Supporting wildlife conservation organizations and initiatives aimed at habitat protection is another essential policy consideration. Comprehensive legislation aimed at balancing human needs and wildlife conservation is vital for ensuring long-term bear safety and fostering sustainable coexistence.
Frequently Asked Questions About Bear Safety
What actions should I take if I encounter a bear?
Remain calm, do not run, and back away slowly while keeping an eye on the bear. Make noise to alert it to your presence, and be prepared to use bear spray if necessary.
How can I reduce the risk of bear encounters while hiking?
Make noise while hiking, travel in groups, and store food properly to minimize attracting wildlife. Understanding bear habitats and behaviors can also help you avoid areas with high bear activity.
Should I play dead during a bear attack?
Yes, if attacked by a grizzly bear, playing dead may be effective. Lie flat on your stomach and cover your neck. However, if a black bear attacks, fighting back is generally advised.
What type of bear spray should I carry?
Select bear spray specifically designed for deterring bears, with a minimum spray distance of 25 feet. Ensure it is easily accessible and know how to use it properly.
What are the indications of an aggressive bear?
Indicators include huffing, jaw popping, and bluff charges. Recognising these behaviors can help you react appropriately during encounters.
How do I assess injuries after a bear attack?
Ensure you are safe from further attacks, then evaluate any wounds. Clean minor injuries and seek medical attention for serious injuries immediately.
Can I report a bear encounter to authorities?
Yes, report encounters to local wildlife management authorities, providing details about the incident to help track bear behavior and prevent future encounters.
What should I do if a bear approaches me?
Stay calm, stand your ground, and prepare to use bear spray. Back away slowly without turning your back on the bear.
How can I educate myself about bear safety?
Participate in local wildlife education programs, attend bear safety workshops, or engage with reliable online resources to learn about bear behavior and safety practices.
What can I do to contribute to community bear safety?
Share your experiences, participate in local education efforts, and promote awareness campaigns about bear safety to help inform and protect your community.
Explore our world on X!
The post Surviving A Bear Attack: Essential Tips appeared first on Survival Bite.
The Article Essential Tips for Surviving a Bear Attack Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
The Article Surviving a Bear Attack: Essential Tips You Need First Appeared ON
: https://ad4sc.com









No responses yet